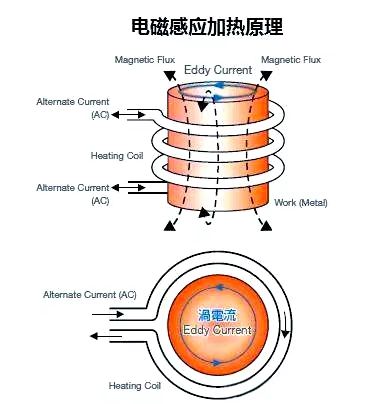
The principle of induction heating is to use electromagnetic induction phenomenon to generate high-density induced current on the surface layer of the workpiece, and then quickly heat the workpiece.
When a certain frequency of alternating current passes through the induction coil, an alternating magnetic field with the same frequency as the current change will be generated inside and outside it.
If a metal workpiece is placed inside an induction coil, under the action of a magnetic field, an induced current with the same frequency as the induction coil but in the opposite direction will be generated inside the workpiece.
Due to the formation of a closed loop along the surface of the workpiece by induced current, it is commonly referred to as eddy current.Eddy currents are mainly distributed on the surface of the workpiece, and there is almost no current passing through the interior of the workpiece. This phenomenon is called surface effect or skin effect. Induction heating, on the other hand, utilizes the skin effect and relies on the current heating effect to rapidly heat the surface of the workpiece.
Specifically, when an alternating magnetic field generates eddy currents in a metal workpiece, due to the resistance of the metal itself, the eddy currents flowing inside the metal will encounter resistance and generate heat. These heats will rapidly increase the temperature of the workpiece, achieving heating of the workpiece. The instantaneous value of induced electromotive force can be expressed as: e = -d\Phi/dt, In the formula, e is the instantaneous potential, \ Pho is the total magnetic flux enclosed by the induced current circuit on the component, which increases with the increase of current intensity in the sensor and the magnetic permeability of the component material, and is related to the gap between the component and the inductor. d \ Pho/dt is the magnetic flux change rate, whose absolute value is equal to the induced potential.
The higher the current frequency, the greater the magnetic flux change rate, and the greater the induced potential. The negative sign in the formula indicates that the direction of the induced potential is opposite to that of the magnetic flux change rate.Induction heating has the advantages of fast heating speed, high efficiency, high energy utilization, precise control of heating temperature and area, and the ability to heat complex shaped workpieces. It is widely used in industrial production for metal melting, forging, heat treatment and other processing technologies.
Jiangyin Zhongyi Electric Co., Ltd.©COPYRIGHT 《中华人民共和国电信与信息服务业务经营许可证》 编号:苏ICP备18035173号-1 苏公网安备 32028102000845号